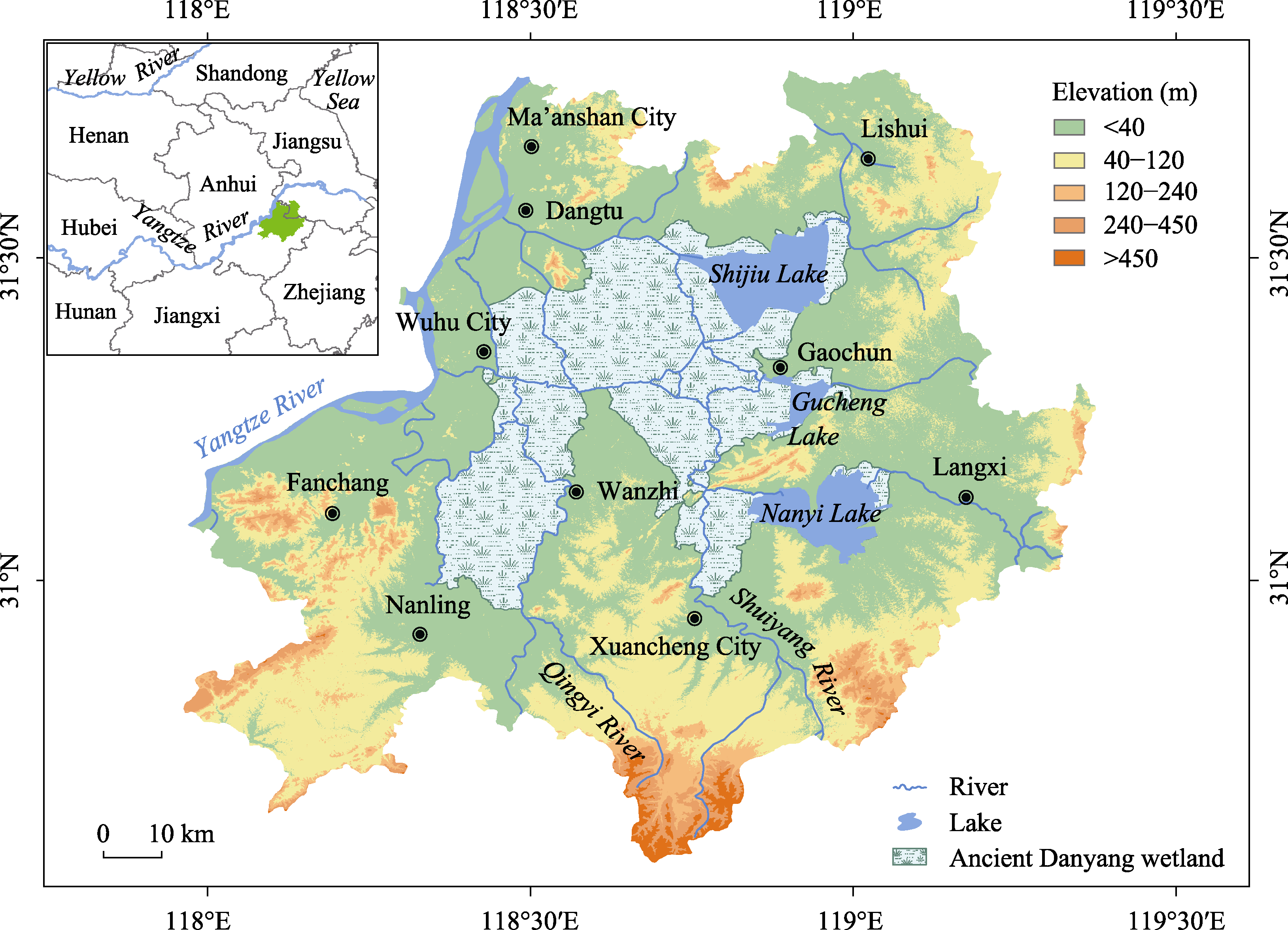
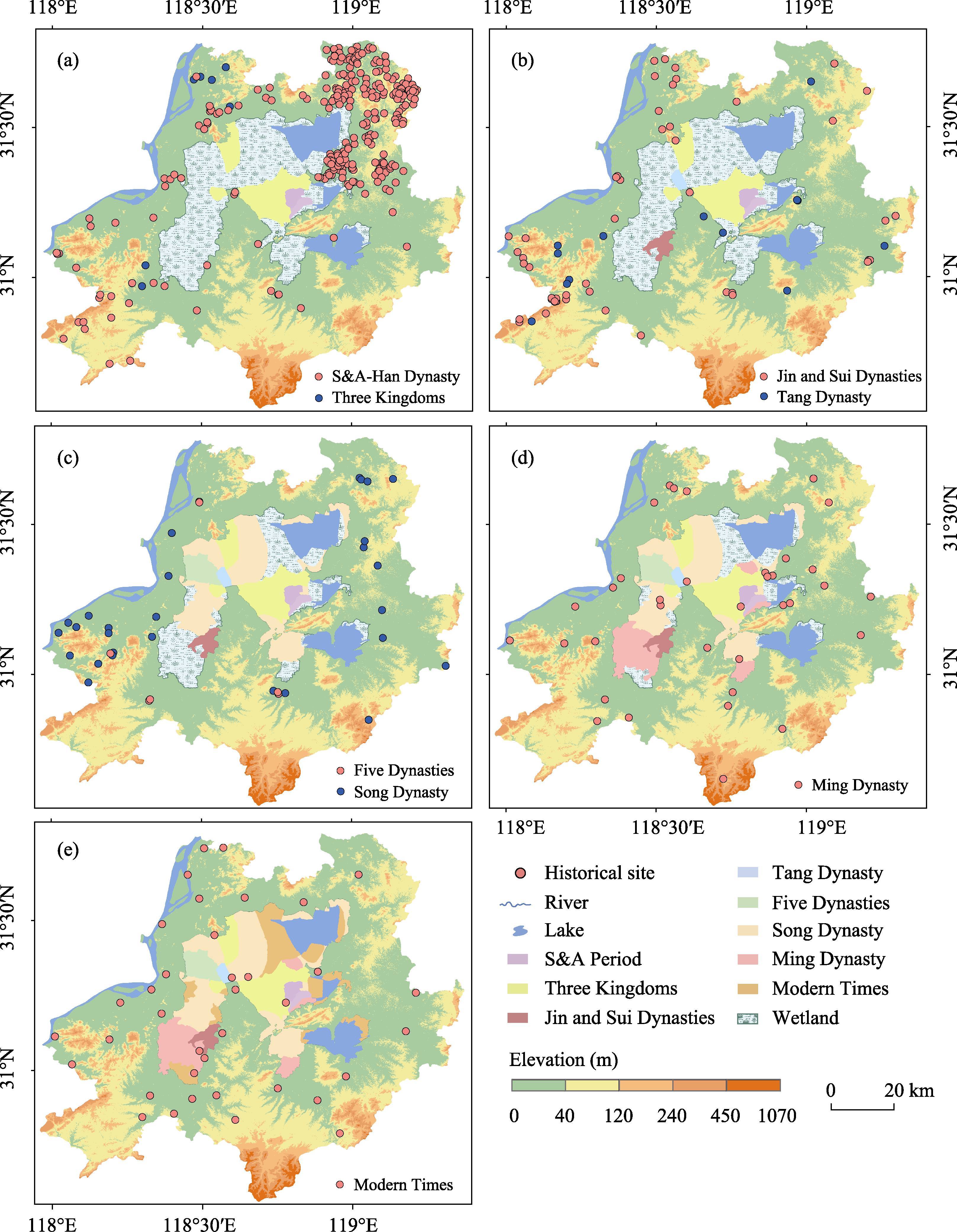
 Figure 4 The distributions of the poldered fields and historical sites varied across different dynasties, including the Spring and Autumn Period to the Three Kingdoms Period (a), the Jin and Sui Dynasties to the Tang Dynasty (b), the Five Dynasties to the Song Dynasty (c), the Ming Dynasty (d) and Modern Times (e) in the study area
Figure 4 The distributions of the poldered fields and historical sites varied across different dynasties, including the Spring and Autumn Period to the Three Kingdoms Period (a), the Jin and Sui Dynasties to the Tang Dynasty (b), the Five Dynasties to the Song Dynasty (c), the Ming Dynasty (d) and Modern Times (e) in the study area
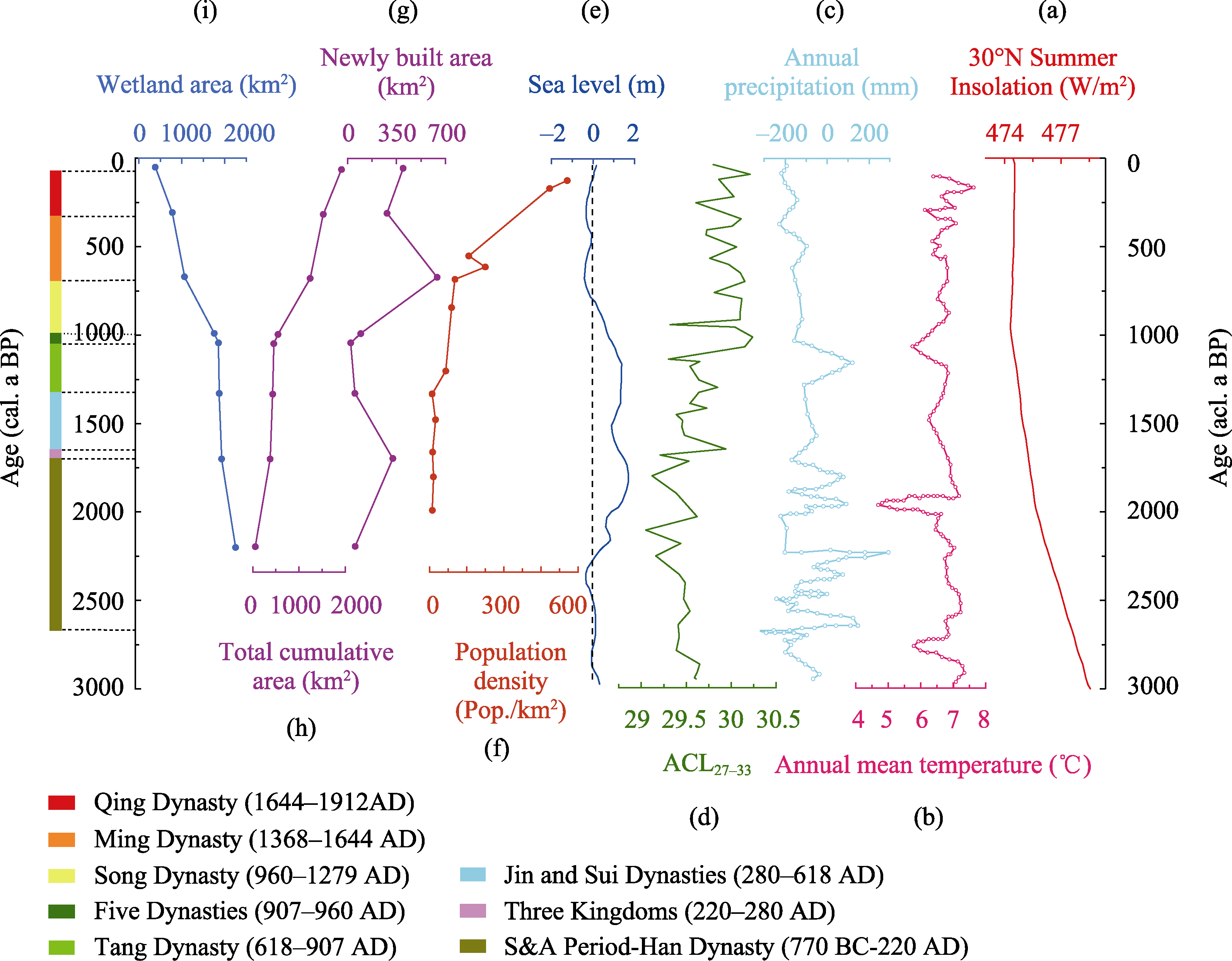 Figure 5 Dynamics on the formation and changes of polder landscapes. (a) Summer insolation at 30°N (W/m2) (Berger and Loutre,
Figure 5 Dynamics on the formation and changes of polder landscapes. (a) Summer insolation at 30°N (W/m2) (Berger and Loutre,