

Journal of Geographical Sciences >
Calculation method for sediment load in flood and non-flood seasons in the Inner Mongolia reach of the Yellow River
*Corresponding author: Wu Baosheng, PhD and Professor, specialized in hydraulics and river dynamics. E-mail: baosheng@tsinghua.edu.cn
Author: Wang Yanjun, PhD Candidate, specialized in geomorphology and fluvial process. E-mail: yanjun1113@126.com
Received date: 2016-01-01
Accepted date: 2016-01-30
Online published: 2016-06-15
Supported by
National Key Basic Research and Development Program of China, No.2011CB403304
National Science and Technology Supporting Plan of the Twelfth Five-year Plan, No.2012BAB02B02
Copyright
Based on an empirical sediment transport equation that reflects the characteristics of “more input, more output” for sediment-laden flow in rivers, a general sediment transport expression was developed, which can take into account the effects of upstream sediment input, previous cumulative sediment deposition, critical runoff for sediment initiation, and the differences in sediment particle sizes between the mainstream and tributaries. Then, sediment load equations for non-flood and flood seasons for the sub-reaches from Bayangaole to Sanhuhekou and from Sanhuhekou to Toudaoguai, as well as the whole Inner Mongolia reach from Bayangaole to Toudaoguai, were formulated based on data collected between 1952 and 2010. The corresponding sediment deposition and the cumulative values at each river reach were calculated using the proposed sediment transport equations for the period 1952 to 2010 according to the principle of sediment conservation. Comparisons between the calculated and measured values using the proposed sediment load equations for the sub-reaches and the entire reach showed that the calculated sediment load and sediment deposition and the corresponding cumulative values in the flood and non-flood seasons were in good agreement with the measured values. These results indicated that the proposed methods can be applied to calculate the sediment load and the associated sediment deposition in the flood and non-flood seasons for long-term trend analysis of sediment deposition in the Inner Mongolia reach of the Yellow River.
WANG Yanjun , WU Baosheng , ZHONG Deyu , WANG Yongqiang . Calculation method for sediment load in flood and non-flood seasons in the Inner Mongolia reach of the Yellow River[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2016 , 26(6) : 707 -721 . DOI: 10.1007/s11442-016-1294-z
Figure 1 Sketch of the Inner Mongolia reach of the Yellow River |
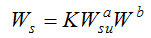
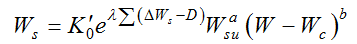
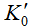 is the basis value of the sediment transport coefficient, reflecting the sediment transport capacity in equilibrium, λ is a coefficient,
is the basis value of the sediment transport coefficient, reflecting the sediment transport capacity in equilibrium, λ is a coefficient, 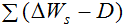 is a parameter of previous cumulative deposition (108 m3),
is a parameter of previous cumulative deposition (108 m3), 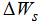 is the erosion and deposition during the calculated period, D is the parameter of the average erosion and deposition (108 t), and Wc is the critical runoff for sediment initiation (108 m3), reflecting the flow energy for the critical sediment initiation. The sediment transport coefficient K in Eq. (1) can now be expressed as follows:
is the erosion and deposition during the calculated period, D is the parameter of the average erosion and deposition (108 t), and Wc is the critical runoff for sediment initiation (108 m3), reflecting the flow energy for the critical sediment initiation. The sediment transport coefficient K in Eq. (1) can now be expressed as follows: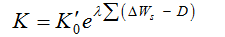

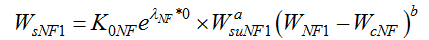
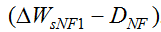 Then the sediment load in the first flood season can be expressed as follows:
Then the sediment load in the first flood season can be expressed as follows: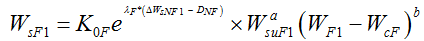
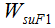 is the upstream sediment input in the first flood season, WF1 is the runoff in the first flood season, and WcF is the critical runoff for sediment initiation in flood seasons.
is the upstream sediment input in the first flood season, WF1 is the runoff in the first flood season, and WcF is the critical runoff for sediment initiation in flood seasons.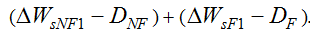 Then, the sediment load in the second non-flood season can be expressed as follows:
Then, the sediment load in the second non-flood season can be expressed as follows: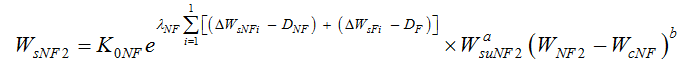
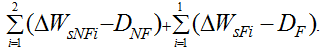 Then, the sediment load expression in the second flood season can be expressed as follows:
Then, the sediment load expression in the second flood season can be expressed as follows: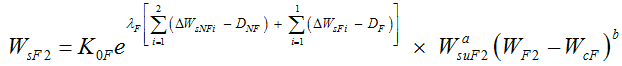
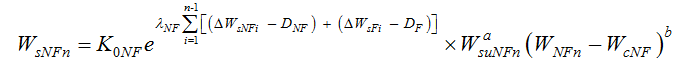
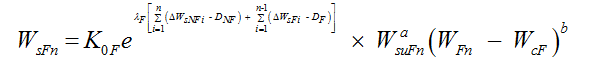
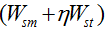
Figure 2 Annual variations in sediment deposition in non-flood and flood seasons in different sections of the Inner Mongolia reach |
Table 1 Average sediment deposition in different sections of the Inner Mongolia reach |
| Year | Period | Annual sediment deposition (108 t) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bayangaole- Toudaoguai | Bayangaole- Sanhuhekou | Sanhuhekou- Toudaoguai | ||
| 1952-1960 | Non-flood season | 0.079 | 0.052 | 0.028 |
| Flood season | 0.894 | 0.374 | 0.520 | |
| 1961-1986 | Non-flood season | 0.014 | 0.020 | -0.034 |
| Flood season | 0.048 | -0.112 | 0.160 | |
| 1987-2010 | Non-flood season | 0.130 | 0.100 | 0.030 |
| Flood season | 0.412 | 0.080 | 0.331 | |
| 1952-2010 | Non-flood season | 0.059 | 0.057 | 0.002 |
| Flood season | 0.325 | 0.040 | 0.285 | |

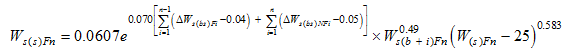
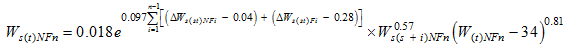
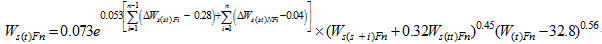
 Ws(st) is the measured sediment deposition of the section from Sanhuhekou to Toudaoguai. Substituting the parameters in Eqs. (13) and (14) into Eq. (3), we can obtain values for the sediment transport coefficient K, which is in the range 0.014 to 0.022 with an average value of 0.017 for non-flood seasons and in the range 0.062 to 0.081 with an average value of 0.070 for flood seasons.
Ws(st) is the measured sediment deposition of the section from Sanhuhekou to Toudaoguai. Substituting the parameters in Eqs. (13) and (14) into Eq. (3), we can obtain values for the sediment transport coefficient K, which is in the range 0.014 to 0.022 with an average value of 0.017 for non-flood seasons and in the range 0.062 to 0.081 with an average value of 0.070 for flood seasons.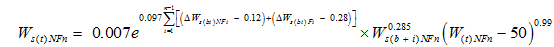
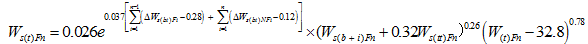
Figure 3 Comparison between calculated and measured sediment loads at Sanhuhekou station based on Eqs. (11) and (12) |
Figure 4 Comparison between calculated and measured sediment loads at Toudaoguai station based on Eqs. (13) and (14) |
Figure 5 Comparison between calculated and measured sediment loads at Toudaoguai station based on Eqs. (15) and (16) |
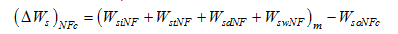
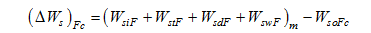
Figure 6 Comparison between calculated and measured amounts of sediment deposition in the river section from Bayangaole to Sanhuhekou (NF: in non-flood season; F: in flood season) |
Figure 7 Comparison between calculated and measured amounts of sediment deposition in the river section from Sanhuhekou to Toudaoguai |
Figure 8 Comparison between calculated and measured amounts of sediment deposition in the river section from Bayangaole to Toudaoguai |
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
Wu,
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |