

Journal of Geographical Sciences >
Relational pattern of urbanization and economic development: Parameter re-evaluation of the Chenery model
*Corresponding author: Zhang Xiaoping (1972-), PhD and Associate Professor, E-mail:zhangxp@ucas.ac.cn
Author: Chen Mingxing (1982-), PhD and Associate Professor, specialized in urbanization and regional development. E-mail:chenmx@igsnrr.ac.cn
Received date: 2014-07-01
Accepted date: 2014-11-02
Online published: 2015-07-17
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China, No.41001080;No.41271184;No.40971075;No.40771054
Copyright
Research has shown that there has been a significant change in the quantitative relationship between urbanization and economic development over the past 50 years. As a result of this change, the Chenery model is no longer capable of performing a comparative analysis of these parameters. We carried out a regression analysis of the normal form of the relation between urbanization and economic development on the basis of the Chenery model. We used empirical data from 149 countries and regions from 1990 to 2009 and adopted the double logarithmic model, introducing a time series variable for urbanization. From 1990 to 2009, with a per capita gross national income remaining between USD 1000 and 10,000, the urbanization rate changed from 17.78 to 60.36% and the relational matching data changed accordingly, although the upper limit of the rate of urbanization remained at about 75%. Urbanization in countries with a smaller population size was more affected by economic development than urbanization in countries with large and medium sized populations.
Key words: Chenery model; economic development; parameter re-evaluation; urbanization
CHEN Mingxing , TANG Zhipeng , BAI Yongping , ZHANG Xiaoping . Relational pattern of urbanization and economic development: Parameter re-evaluation of the Chenery model[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2015 , 25(8) : 991 -1002 . DOI: 10.1007/s11442-015-1215-6
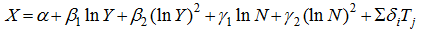
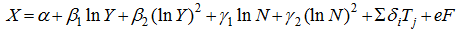
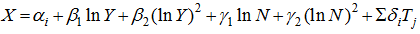
Table 1 Differences in levels of urbanization at different income levels |
| Per capita income (USD) | <100 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 800 | 1000 | >1000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urbanization rate (%) | 12.8 | 22.0 | 36.2 | 43.9 | 49.0 | 52.7 | 60.1 | 63.4 | 65.8 |
Note: The median value of nations with a per capita income below USD 100 is USD 70 and for nations with a per capita income above USD 1000, USD 1500 is taken. |
 Large country - a total of 11 countries with a population >100 million (China, India, the USA, Indonesia, Brazil, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nigeria, Russia, Japan and Mexico), giving a total population of 4.08 billion and accounting for 63.4% of the total population in the whole sample;
Large country - a total of 11 countries with a population >100 million (China, India, the USA, Indonesia, Brazil, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nigeria, Russia, Japan and Mexico), giving a total population of 4.08 billion and accounting for 63.4% of the total population in the whole sample; Medium country - a total of 60 countries or regions with a national population <100 million but >10 million, with a total population of 2.07 billion and accounting for 32.2% of the total population in the whole sample;
Medium country - a total of 60 countries or regions with a national population <100 million but >10 million, with a total population of 2.07 billion and accounting for 32.2% of the total population in the whole sample; Small country - a total of 78 countries or regions with a national population is <10 million, with a total population of 280 million and accounting for 4.4% of the total population in the whole sample.
Small country - a total of 78 countries or regions with a national population is <10 million, with a total population of 280 million and accounting for 4.4% of the total population in the whole sample.Table 2 Characteristics of the empirical data of the 149 countries in 1990-2009 |
| No. of countries by size of population | Index | Sample | Min. | Max. | Median | Average | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (149) | Urbanization | 2980 | 5.4 | 100 | 53.5 | 52.1 | 23.6 |
| Economic level | 2980 | 200 | 67,200 | 4540 | 8832.6 | 10,443.6 | |
| Large country (11) | Urbanization | 220 | 19.8 | 86.0 | 46.5 | 52.3 | 21.4 |
| Economic level | 220 | 500 | 47,100 | 3230 | 8877.8 | 11,284.2 | |
| Medium country (60) | Urbanization | 1200 | 8.9 | 97.4 | 53.9 | 51.4 | 23.7 |
| Economic level | 1200 | 200 | 41,720 | 4115 | 7932.5 | 9380.3 | |
| Small country (78) | Urbanization | 1560 | 5.4 | 100 | 53.2 | 52.7 | 23.8 |
| Economic level | 1560 | 290 | 67,200 | 4960 | 9518.6 | 11,034.6 |
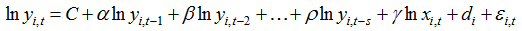
Table 3 Parameter estimates and test of the regression model |
| Type (lag period) | C | α | β | γ | R2 | adjR2 | DW | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (2) | 0.0246*** (10.476) | 1.8131*** (166.307) | -0.8215*** (-77.645) | 0.0011*** (6.607) | 0.9999 | 0.9999 | 2.13 | 1359778*** |
| Large country (2) | 0.0153*** (3.799) | 1.8299*** (41.603) | -0.8349*** (-19.259) | 0.0007** (2.586) | 0.9999 | 0.9999 | 2.12 | 5134722*** |
| Medium country (2) | 0.0088*** (3.786) | 1.8628*** (127.176) | -0.8661*** (-60.529) | 0.0006*** (3.215) | 0.9999 | 0.9999 | 2.15 | 4437116*** |
| Small country (2) | 0.0347*** (8.584) | 1.7940*** (115.203) | -0.8052*** (-53.523) | 0.0011*** (4.298) | 0.9999 | 0.9999 | 2.13 | 831196*** |
Note: *** and ** represents the significance level in 1% and 5%, and t statistics of each parameter is in the blocks. |
Figure 1 Urbanization and economic development in 1990-2009 |
Table 4 Comparison of the new model for 1990-2009 data and the Chenery model |
| Similar per capita GNI | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per capita GNI($) | <100 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 800 | 1000 | >1000 | |
| Chenery | Urbanization rate (%) | 12.8 | 22.0 | 36.2 | 43.9 | 49.0 | 52.7 | 60.1 | 63.4 | 65.8 |
| New relationship pattern | - | 11.8 | 12.2 | 12.8 | 13.3 | 14.0 | 16.1 | 17.8 | - | |
| Similar urbanization rate | ||||||||||
| Urbanization rate (%) | 12.8 | 22.0 | 36.2 | 43.9 | 49.0 | 52.7 | 60.1 | 63.4 | 65.8 | |
| Chenery | Per capita GNI ($) | <100 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 800 | 1000 | >1000 |
| New relationship pattern | 300 | 1500 | 2900 | 3900 | 4900 | 5800 | 9800 | 13,400 | 17,000 | |
Table 5 New pattern of level of urbanization and economic development in 1990-2009 |
| Per capita GNI (USD) | 1000 | 2000 | 3000 | 4000 | 5000 | 6000 | 7000 | 8000 | 9000 | 10000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urbanization rate (%) | 17.78 | 27.36 | 36.82 | 44.30 | 49.60 | 53.24 | 44.20 | 57.68 | 59.15 | 60.36 |
| Per capita GNI (USD) | 12,000 | 14,000 | 16,000 | 18,000 | 20,000 | 22,000 | 24,000 | 26,000 | 28,000 | 30,000 |
| Urbanization rate (%) | 62.31 | 63.87 | 65.21 | 66.38 | 67.42 | 68.37 | 69.23 | 70.03 | 70.77 | 71.46 |
Figure 2 Impact of national population size and economic development on level of urbanization |
Figure 3 Distribution rate of urbanization in countries with different sizes of population |
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |