

Journal of Geographical Sciences >
Spatial energy efficiency patterns and the coupling relationship with industrial structure: A study on Liaoning Province, China
Author: Guan Wei (1959-), Professor, specialized in regional economy and industrial planning. E-mail:lsgw2000@sina.com
Received date: 2014-07-04
Accepted date: 2014-08-20
Online published: 2015-03-15
Supported by
The MOE Project of Key Research Institute of Humanities and Social Sciences in University, No.14JJD790044
Science and Technology Research Program Supported by the Education Department of Liaoning Province, No.L2013411
Copyright
Using a sample of 14 prefecture-level cities in Liaoning Province, this study first explored the spatial hierarchy and structural characteristics of energy efficiency from the following three viewpoints: energy technical efficiency based on data envelopment analysis, energy consumption per unit of GDP, and energy utilization efficiency combining the previous two indexes. After measuring and analyzing the advancement, rationality, and concentration of the industrial structure in each city, we made some generalizations about the coupling features of the energy efficiency and industrial structure in Liaoning, using the coupling degree rating model. Some of our conclusions are as follows: (1) The 14 cities differ significantly in their energy efficiency, with Shenyang, Dalian, Anshan, and Jinzhou enjoying the highest energy efficiency. Northwestern Liaoning and other heavy-industrial cities such as Fushun and Benxi belong to low-efficiency and high-consumption areas. (2) In areas with higher efficiency, the spatial patterns of the energy technical efficiency, energy consumption per unit of GDP, and energy utilization efficiency are, respectively, "π"-,"Ⅱ"- and "H"- shaped. Geographically, the energy utilization efficiency shows different trends from east to west and from north to south. Factors such as the binuclear structure of economic development have a major effect on this spatial pattern of energy efficiency. (3) Southeastern Liaoning enjoys a highly advanced industrial structure. Areas with a highly rational industrial structure form an “H” shape, with Shenyang and Dalian at the two poles. The urban agglomerations in middle and southern Liaoning have a highly concentrated industrial structure. (4) Overall, the coupling between energy efficiency and industrial structure is low in Liaoning, except for Shenyang and Dalian at both ends, where the coupling between an advanced industrial structure and energy efficiency is higher than in other cities.
Key words: energy efficiency; industrial structure; spatial patterns; coupling
GUAN Wei , XU Shuting . Spatial energy efficiency patterns and the coupling relationship with industrial structure: A study on Liaoning Province, China[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2015 , 25(3) : 355 -368 . DOI: 10.1007/s11442-015-1173-z
Figure 1 Grade distribution of energy efficiency in Liaoning Province |
Figure 2 Trend distribution of energy efficiency in Liaoning Province |
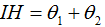 , whereθ1 denotes the effect of the transformation of a primary industry to a secondary and tertiary industry. The greater the value ofθ1 andθ2, the higher the transfer level is. The greater the value of IH, the higher the level of industrial structure is.
, whereθ1 denotes the effect of the transformation of a primary industry to a secondary and tertiary industry. The greater the value ofθ1 andθ2, the higher the transfer level is. The greater the value of IH, the higher the level of industrial structure is. 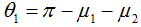 .μ1 andμ2 denote the vector angles from (x1, x2, x3) to (0, 1, 0) and from (x1, x2, x3) to (0, 0, 1), respectively. x1, x2, and x3 denote, respectively, the proportion of primary, secondary, and tertiary industries’ value added in GDP.
.μ1 andμ2 denote the vector angles from (x1, x2, x3) to (0, 1, 0) and from (x1, x2, x3) to (0, 0, 1), respectively. x1, x2, and x3 denote, respectively, the proportion of primary, secondary, and tertiary industries’ value added in GDP. 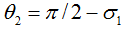 .σ1 denotes the vector angle between (x2, x3) and (0, 1). The following is the calculation formula for the two- and three-dimension angles.
.σ1 denotes the vector angle between (x2, x3) and (0, 1). The following is the calculation formula for the two- and three-dimension angles.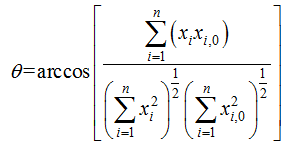
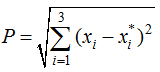
Figure 3 Spatial distribution of industrial structure in Liaoning Province |
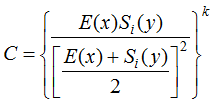
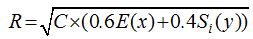
Table 1 The reference standard of coupling & coordinating stage |
| Coupling degree | Coupling stage | Coupling coordination degree | Coupling coordination degree | Comprehensive coordination stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0<C≤0.3 | Separate stage | 0<R≤0.3 | Low coupling coordination stage | Low coordination separate stage |
| 0.3<C≤0.5 | Antagonistic stage | 0.3<R≤0.5 | Middle coupling coordination stage | Middle coordination antagonistic stage |
| 0.5<C≤0.8 | Run-in stage | 0.5<R≤0.8 | High coupling coordination stage | High coordination run-in stage |
| 0.8<C≤1 | Coupling stage | 0.8<R≤1 | Extreme coupling coordination stage | Extreme coordination coupling stage |
Figure 4 Coupling distribution of energy efficiency and industrial structure |
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |