

Journal of Geographical Sciences >
Aridity trend and response to vegetation restoration in the loess hilly region of northern Shaanxi Province
*Corresponding author: Lu Changhe (C.H.Lu), Professor, E-mail:luch@igsnrr.ac.cn
Author: Li Wangjun, PhD Candidate, E-mail:liwj.10b@igsnrr.ac.cn
Received date: 2014-01-07
Accepted date: 2014-03-22
Online published: 2015-03-15
Supported by
National Basic Research Program of China, No.2012CB955304
Copyright
Detecting variation trend in dry-wet conditions can provide information for developing strategic measures to mitigate the impacts of global warming, particularly in dry regions. Taking the hilly region of northern Shaanxi on the Loess Plateau as a case area, this study analyzed the trend of aridity variation during 1981-2012, and explored the effect of vegetation restoration promoted by the Grain-for-Green (GFG) program implemented in 1999. The results indicated that the aridity in the region was non-significantly increased by 0.88% per year during 1981-2012, showing a drying trend. This drying trend and amplitude were changed by the influence of vegetation restoration promoted by the GFG program, based on two findings. The first one was that the aridity variation tended to increase during 1981-1999 while it turned to decrease during 2000-2012, with the regional mean relative change rate changed from 2.45% to -1.06%. This distinction was more remarkable in the loess gully region, where the vegetation was improved more obviously. The second one was that the mean vegetation coverage as indicated by EVI increased by 0.90% to 4.32% per year at county level, while the aridity decreased by 0.14% to 2.32% per year during 2000-2012. The regression analysis using the mean county data indicated that the change rate of aridity was negatively related to that of EVI with the coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.56, illustrating that around half of the aridity decline was explained by the EVI change. The mechanism of this effect was complicated, but it was found that the wind speed decline induced by the vegetation improvement could be an important contributor. It is concluded that the region became drier during 1981-2012, but the eco-restoration reduced the drying speed. However, this conclusion is involved in uncertainties, and further study based on experiments is needed to confirm the effect of the GFG-promoted vegetation restoration.
Key words: aridity; variation trend; hilly Loess Plateau; Grain-for-Grain program
LI Wangjun , LU Changhe . Aridity trend and response to vegetation restoration in the loess hilly region of northern Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2015 , 25(3) : 289 -300 . DOI: 10.1007/s11442-015-1168-9
Figure 1 Location of the study area |
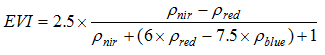
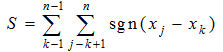
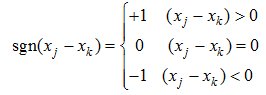
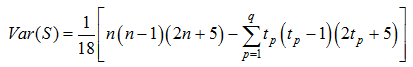
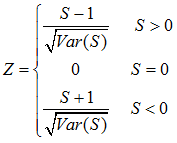
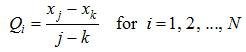
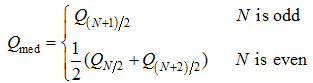
Table 1 Mean and coefficient of variation (CV) of aridity during 1981-2012 |
| Hequ | Yulin | Yanchi | Dingbian | Wuqi | Hengshan | Suide | Yan’an | Luochuan | Tongchuan | Yaoxian | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aridity | 1.66 | 1.89 | 2.85 | 2.56 | 1.28 | 2.25 | 1.95 | 1.23 | 1.08 | 1.07 | 1.38 |
| CV | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.38 | 0.22 |
Note: Dingbian, 1989-2012; Tongchuan, 1981-1999; Yaoxian, 2000-2012 |
Figure 2 Spatial distribution of mean aridity (a) and precipitation (mm) (b) during 1981-2012 |
Table 2 Test statistic Z and slope Q values at different stations during 1981-2012, 1981-1999 and 2000-2012, respectively |
| Station | 1981-2012 | 1981-1999 | 2000-2012 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z | Q | Z | Q | Z | Q | |
| Hequ | 1.09 | 0.011 | 0.84 | 0.023 | -0.79 | -0.010 |
| Yulin | 0.96 | 0.007 | 1.26 | 0.023 | 0.43 | 0.010 |
| Yanchi | -0.02 | -0.001 | -0.49 | -0.011 | -0.31 | -0.049 |
| Dingbian | na | na | na | na | -0.67 | -0.050 |
| Wuqi | 0.92 | 0.006 | 0.84 | 0.014 | 0.06 | 0.005 |
| Henshan | 0.18 | 0.003 | 2.38* | 0.052 | -0.92 | -0.067 |
| Suide | 0.96 | 0.009 | 1.82+ | 0.040 | -1.65+ | -0.051 |
| Yan’an | 1.28 | 0.007 | 1.96+ | 0.030 | -0.92 | -0.015 |
| Luochuan | 0.76 | 0.003 | 1.47 | 0.020 | 0.31 | 0.004 |
| Tongchuan | na | na | 1.61 | 0.021 | na | na |
| Yaoxian | na | na | na | na | -1.40 | -0.031 |
Note: + and *: significant at the 0.1 and 0.05 significance level, respectively. na: not available |
Figure 3 Spatial distribution of Z values during periods of 1981-2012 (a), 1981-1999 (b) and 2000-2012 (c) |
Figure 5 Spatial distribution of the trend of EVI variation during 2000-2012(Decreased significantly, Z≤-1.96; decreased non-significantly, -1.96<Z<0; increased significantly, Z≥1.96; increased non-significantly, 0<Z< 1.96) |
Figure 4 Spatial distribution of the relative change rate (%) during 1981-2012 (a), 1981-1999 (b) and 2000-2012 (c) |
Figure 6 Regression relationship between relative change rates of aridity and EVI at county level |
Figure 7 Regression relationship of mean (a) and maximum (b) wind speed (m/s) with EVI during 2000-2012 |
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
|
| 41 |
|
| 42 |
|
| 43 |
|
| 44 |
|
| 45 |
|
| 46 |
|
| 47 |
|
| 48 |
|
| 49 |
|
| 50 |
|
| 51 |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |