

Journal of Geographical Sciences >
Non-stationary water-level fluctuation in China’s Poyang Lake and its interactions with Yangtze River
*Corresponding author: Wan Rongrong (1977-), PhD and Associate Professor, specialized in watershed eco-hydrology, environmental impacts of land use and cover changes at watershed scale. E-mail:rrwan@niglas.ac.cn
Author: Dai Xue (1988-), MS, specialized in watershed hydrology and ecological effects. E-mail:daixue1224@163.com
Received date: 2014-05-06
Accepted date: 2014-07-02
Online published: 2015-03-15
Supported by
National Basic Research Program of China (“973” Program), No.2012CB417006
National Natural Science Foundation of China, No.41171024;No.41271500
Copyright
Seasonal water-level fluctuations (WLF) play a dominate role in lacustrine ecosystems. River-lake interaction is a direct factor in changes of seasonal lake WLF, especially for those lakes naturally connected to upstream and downstream rivers. During the past decade, the modification of WLF in the Poyang Lake (the largest freshwater lake in China) has caused intensified flood and irrigation crises, reduced water availability, compromised water quality and extensive degradation of the lake ecosystem. There has been a conjecture as to whether the modification was caused by its interactions with Yangtze River. In this study, we investigated the variations of seasonal WLF in China’s Poyang Lake by comparing the water levels during the four distinct seasons (the dry season, the rising season, the flood season, and the retreating season) before and after 2003 when the Three Gorge Dam operated. The Water Surface Slope (WSS) was used as a representative parameter to measure the changes in river-lake interaction and its impacts on seasonal WLF. The results showed that the magnitude of seasonal WLF has changed considerably since 2003; the seasonal WLF of the Poyang Lake have been significantly altered by the fact that the water levels both rise and retreat earlier in the season and lowered water levels in general. The fluctuations of river-lake interactions, in particular the changes during the retreating season, are mainly responsible for these variations in magnitude of seasonal WLF. This study demonstrates that WSS is a representative parameter to denote river-lake interactions, and the results indicate that more emphasis should be placed on the decrease of the Poyang Lake caused by the lowered water levels of the Yangtze River, especially in the retreating season.
DAI Xue , WAN Rongrong , YANG Guishan . Non-stationary water-level fluctuation in China’s Poyang Lake and its interactions with Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2015 , 25(3) : 274 -288 . DOI: 10.1007/s11442-015-1167-x
Figure 1 Location and geological map of the Poyang Lake |
Figure 2 The monthly mean water level at Xingzi Station during 1951-2011 |
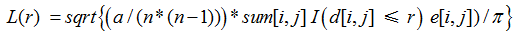
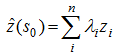
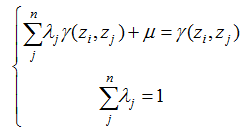
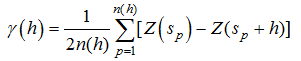
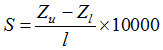
Figure 3 The spatial point pattern of hydrological stations in the Poyang Lake tested by the L-function |
Figure 4 Mean lake-levels of the rising, flood, retreating, and dry season during periods of 1980-2002 and 2003-2011 |
Figure 5 The mean water surface slope of Hukou-Xiangzi lake region (a) and Duchang-Kangshan lake region (b) in 1980-2002 and 2003-2011 |
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |